BACKGROUND
The Adyar Creek and the Estuary from the eastern part of Thiru. Vi. Ka. Bridge covers an area of about 358 acres. This unique eco system has supported a wide variety of flora and fauna which gradually degraded over the years. The Government ordered to restore the eco system and to develop an Eco park in 58acres (the Survey Nos.4309/1, 2 & 8 covering an extent of 1047 Grounds and 1256 Sq.ft) in Phase I restore the balance 300 acres in Phase II. The Phase I of the programme, named Adyar Poonga, is a section of an inland waterway coming from the Adyar Estuary, curving its way along the Quibble Island up to the Greenways Road. A survey of historic plans shows that the area has functioned as a storm water outflow for the watershed around the Creek, mainly for Mandaveli. Storm water coming from the surrounding areas through storm water drains would fill the Creek and functioned as retention and infiltration pond and excess overflows to the estuary. Similarly the area served as a reservoir for tidal water in times of high tide levels. Of late, the Creek was used as a place of disposal of sewage and dumping of solid waste.
Since 1997, the Government of Tamil Nadu had been contemplating to protect the Creek and creation of an Eco Park to restore the ecological balance and raise public awareness on environmental issues. The Government appointed the Tamil Nadu Urban Infrastructure Financial Services Ltd., Chennai (TNUIFSL) to identify and engage necessary consultants for the preparation of a concept/master plan, detailed planning and implementation for the development of the Eco- Park.
Consultant was appointed as consultants for developing a Master Plan. Several reputed specialist consultants worked on this project in the fields of water management, flora and fauna habitat mapping, wetland ecology, architecture and landscaping.
LOCATION
The creek begins near the Chetinnad Palace, extends northward into the mainland and takes a complete U-turn near the Foreshore Estate and ends near Mandavelipakkam. It surrounds what was formerly called Quibble Island. The total area of the Adyar Poonga covers 58 acres and it is limited by Greenways road to the south, Town Planning Scheme road on the northwest, South Canal Bank road in the north east and Santhome Causeway bridge to the east.
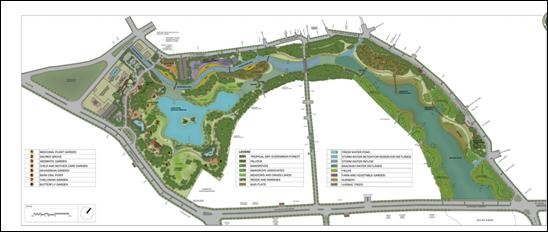
Restoration Plan of Adyar Creek (58 acres)
OBJECTIVES
The objectives of Eco-Restoration programme are
- To restore the degraded area and re-habilitate the coastal ecology of Adyar Creek.
- To rehabilitate the watershed of Adyar Creek with minimum interface of public for sustainable maintenance.
- To emphasize and introduce environmental education with Adyar Poonga as a research base.
RESTORATION ACTIVITIES
The restoration activities has been commenced in January 2008 and completed in January 2010.
Excavation to increase in Water Spread Area
As a first step to proceed with the eco-restoration, about 2.80 lakhs cu.m of accumulated sludge and debris in the water body have been excavated. After retaining some quantity of excavated soil for landscaping and plantation activities, the balance quantity has been taken out of Poonga. The land use and land cover map of this area prepared in July, 2007 clearly shows that the water spread of the creek was 5.53 %only. After restoration, it is measured in January 2011 that the creek has 59% of the water spread. Removal of debris and sludge has facilitated the ecological function of creek.
Arresting of Sewage discharge from outfalls
There are seven storm water drain outfalls entering into the Poonga. Before the implementation of eco-restoration activities, these storm water drains were misused for sewage discharge. During restoration, the sewage is diverted into sewer pipeline with the assistance of Chennai Metropolitan Water Supply and Sewerage Board and Chennai Corporation to prevent the sewage inflow into the Poonga.
Land Development
A small portion of the earth excavated from the project area has been utilized to create mounds around the water body, which supports coastal vegetation such as intertidal plants like mangroves, mangrove associates, reeds and terrestrial plants. It also serves as niche for birds and other terrestrial animals of creek ecosystem. These mounds also serve as sound barriers against vehicular traffic and aid in realizing tranquillity in the project area.
Recreating Vegetation
The plantation at Adyar Poonga comprises of six vegetative elements such as trees, shrubs, herbs, grasses, climbers and aquatic plants for planting in aquatic zone, core zone, peripheral zone, inland and littoral zone, along water margins and hedges, grass cover, specimen tree, rockery etc. About 1,10,161 plants belonging to 172 species are planted to provide a green cover and typical vegetation of the Coromandal coast surrounding the water bodies.
Animal Diversity
The success of the restoration can be measured by species diversity, density and abundance of faunal elements in an area. In 2007, 65 species of vertebrates was recorded viz., Fish (5 species), Amphibians (3 species), Reptiles (11 species), Birds (33 species) and Mammals (13 species). During restoration process, the water-bodies have been protected from any external source of pollution. Also, the site was protected from hunting and vandalism of the habitat of birds and reptiles. This has facilitated the increase in diversity to 159 species. As on June 2012, 27 species of Fish, 10 species of Amphibians, 19 species of Reptiles, 90 species of Birds and 13 species of Mammals are recorded in Adyar Poonga.
FACILITIES
Arrival and Orientation
The arrival and orientation zone has been created to provide orientation about the Poonga with site maps and signage depicting the different features of the ecological park. About 318 educational signage on Cuddapah stone slabs, 18 educational signage on marine plywood and 751 plant signage, 100 directional signage and 54 artifacts depicting various forms of animals have been painted and erected at appropriate places to navigate and educate the visitors about the Poonga.
Interactive Learning Space
In the Interactive Learning space, earthen berms have been made showcasing the creek animals made out of eco-friendly materials. A space is provided for conducting environmental education programs and related activities. In addition, arrangements have been made to facilitate the visitors to sit and enjoy the Poonga.
Nursery Centre
The Nursery has been developed with medicinal and indigenous plants. There are signages to describe the medicinal properties of the plants. The plants raised here will be utilized for replacement of dead plants in the Poonga.

Environmental Education Centre
The dilapidated Fisheries Training Institute inside the Poonga is rebuilt as an Environmental Education Centre where programs for visiting school children are being conducted. A series of programs designed to explain the basic principles of ecology with an emphasis on coastal ecology and watershed rehabilitation, to familiarise with plants and animals native to Chennai and learn how human activities affect the environment.

Pedestrian Bridge
A bridge was reconstructed (by demolishing the existing damaged bridge) connecting Karpagam Avenue and Mandaveli for the use of Pedestrian.
Appropriate Technology Centre
Solar lighting system have been installed at the entrance plaza, Environmental Education Centre, Nursery, pathways and parking area to demonstrate green energy concepts. A demonstration wind mill has been installed to showcase the use of wind energy for water pumping. A demonstration wastewater treatment plant of 15000 litre capacity has been constructed to recycle the water by treating wastewater generated from nearby toilet complex and to use the treated water for irrigation purposes.
Environmental Education Programme
Environmental Education is life-long learning processes that provide leadership in the development of learning opportunities that empower students and teachers to develop skills needed to make wise environmental decision and responsible actions against ecological issues. Adyar Eco Park is an Eco-Restoration Park basically functioning as a Centre for Environmental Education and Research. Therefore, it is engaged in educating school students and teachers in various Environmental Education activities particularly the importance of restoration and conservation of wetlands. Only school childrens with teachers are allowed in the Eco Park and guided tour is being undertaken. Adyar Eco Park offer variety of Environmental Education Programme to school students particularly for the Government High School, Higher Secondary School, Chennai High School and Higher Secondary Schools whom the opportunity is not available. Adyar Eco Park also celebrating the world ecological significance day such as World Wetland Day, World Environment Day and Wildlife Week Celebration.

